Predicting the expression levels of genes by epigenetic marks
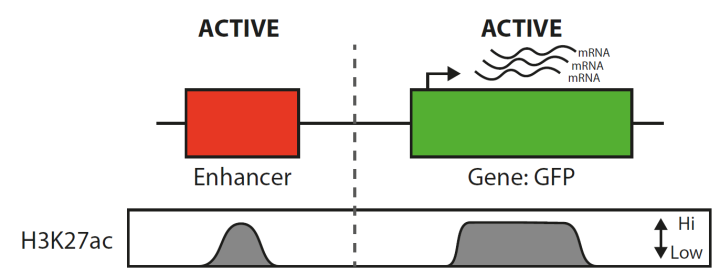
Aim: Our recent experiments with increasing collagen expression by inhibiting DNA methylation have shown an additional but interesting result. We showed that the epigenetic mark H3K27ac puts enhancers and genes into an ACTIVE state. Using this information along with what we know from other epigenetic marks we aim to predict the expression levels of genes based on their epigenetic marks.
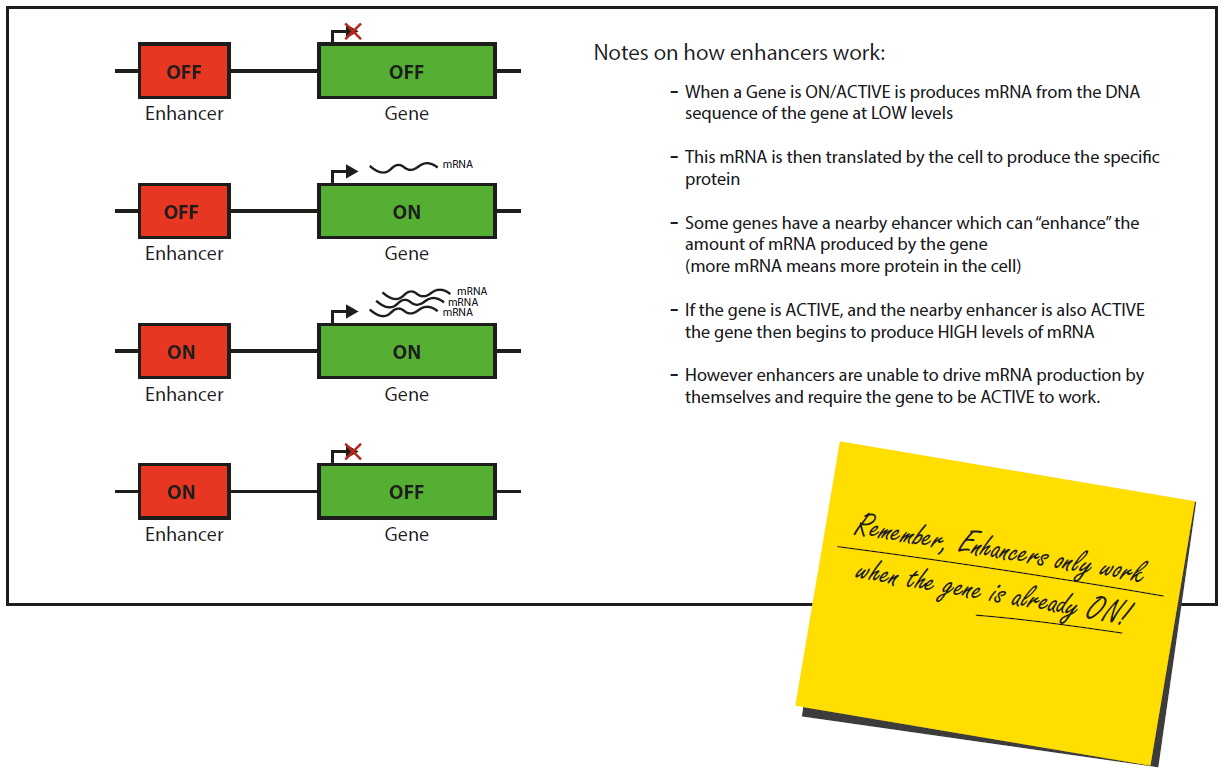
To help I have compiled information on how enhancers work with genes and what we now know about epigenetic marks at ACTIVE and INACTIVE DNA regions.